Hernia Repair: Inguinal, Umbilical & Incisional Hernias

Hernia Surgery: Innovation and Optimal Recovery
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. It can develop in different areas of the body, but it is most commonly found in the abdomen and groin.
Hernias can be congenital (present from birth) or acquired due to factors such as excessive physical strain, obesity, aging, or previous surgeries.
Types of Hernias and Their Characteristics
🔹 Inguinal hernia: The most common type, primarily affecting men. It occurs in the groin and can be direct or indirect.
🔹 Umbilical hernia: Appears in the navel area, often affecting women after pregnancy or people with increased intra-abdominal pressure.
🔹 Femoral hernia: More common in women, located in the upper thigh, and carries a higher risk of strangulation.
🔹 Incisional hernia: Develops at the site of a previous surgical incision and may grow over time, affecting mobility.
🔹 Epigastric hernia: Found between the sternum and the navel, usually containing fatty tissue and posing a risk of strangulation.
🔹 Hiatal hernia: Occurs when part of the stomach moves into the chest through the diaphragm. For more information, visit the dedicated section on our website.
Symptoms and Complications of a Hernia
Symptoms may vary depending on the type and severity of the hernia, but the most common include:
🔹 Visible bulge in the affected area, which may increase in size with physical effort.
🔹 Discomfort or pain, especially when lifting heavy objects, coughing, or engaging in physical activity.
🔹 A feeling of tightness, swelling, or burning in the affected area.
🔹 In inguinal hernias, pain may radiate toward the testicle in men.
🔹 In hiatal hernias, symptoms may include acid reflux and heartburn.
Potential complications if left untreated:
🔹 Strangulation: When part of the tissue becomes trapped, cutting off blood supply and potentially leading to necrosis.
🔹 Intestinal obstruction: Some abdominal hernias can trap part of the intestine, blocking normal food passage and causing severe pain, vomiting, and abdominal bloating.
🔹 Infections and abscesses: In more advanced cases, a hernia can lead to serious infections.
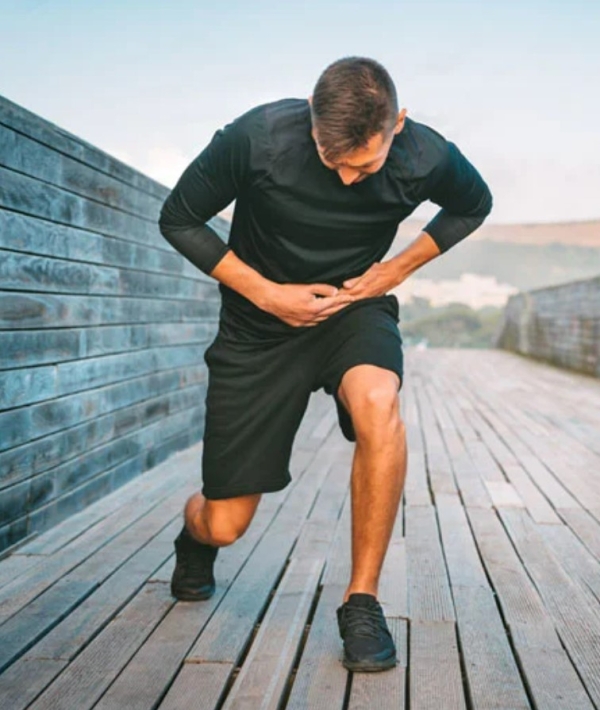
Surgical Treatment: What is Hernioplasty?
Hernioplasty is the surgical procedure used to repair hernias. There are two main techniques:
Traditional Open Surgery 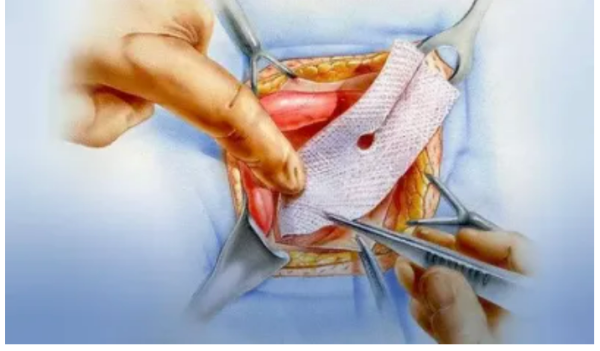
The surgeon makes an incision in the affected area to reposition the protruding tissue and reinforce the abdominal wall with sutures or a synthetic mesh.
🔹 Direct visualization of the hernia.
🔹 Suitable for large or complex hernias.
🔹 Longer recovery time and possible visible scarring.
Laparoscopic Surgery (Minimally Invasive)
This technique involves making small incisions to insert a camera and specialized surgical instruments, allowing for a precise repair with minimal tissue damage.
🔹 Less postoperative pain.
🔹 Faster recovery.
🔹 Minimal scarring and reduced risk of infection.
🔹 May not be suitable for all cases.
How to Choose the Best Treatment?
The choice between open or laparoscopic surgery depends on:
🔹 Type and location of the hernia.
🔹 Size and complexity of the hernia defect.
🔹 Patient’s surgical history and overall health condition.
During your consultation, we will evaluate your case and recommend the most appropriate treatment to ensure safety, effectiveness, and a quick recovery.
Your Health, Our Priority
Hernia repair surgery is a safe and well-established procedure backed by years of medical experience. Thanks to advanced techniques, such as laparoscopy, we can offer an effective solution with faster recovery and minimal invasiveness.
📧 Contact us for more information or to schedule a consultation. We are here to help you make the best decision for your health.
Patients Reviews
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Dr. Alevizos is incredible. He explains everything patiently and always with a great attitude. From the very first minute, he made me feel calm and in good hands. You can tell he genuinely cares about how you’re doing and not just about solving the problem quickly. If you’re looking for a surgeon who truly cares about you and is amazing at what he does, he’s the one.
Carlos B
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ A great professional from the very beginning. During the consultations, he thoroughly understood my case, always approachable and reassuring. The procedure went as well as expected, and with the treatment I’m following, I’ve improved significantly.
I’m truly grateful to have been in good hands.
Manu P
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ For me, it has been an enormous stroke of luck to put myself in his hands for a pathology that is so difficult to treat and complicated to resolve. My most sincere thanks and all my love to Dr. Alevizos
NGQ
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ I have been operated on twice by Dr. Alevizos, and without a doubt, he is a great professional who is caring and deeply involved with his patients. I felt absolute peace of mind in his hands. Thank you for everything, Dr. Leonidas!
Francisco J
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Without a doubt, Dr. Leonidas is a spectacular surgeon, in addition to providing gentle, kind and reliable treatment. I was lucky enough to be operated on by him for a pilionidal cyst after having previously been operated on twice without obtaining good results... until I put myself in the hands of Dr. Leonidas, who thanks to his intervention after almost two years, I am in perfect condition. been and I haven't had any problems again!
Alejandro R
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ His patience, kindness, and professionalism throughout the whole process—from diagnosis to surgery and discharge—gave me peace of mind and helped me cope in the best possible way.
Truly grateful
MTT
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐I had stomach surgery by surgeon Leonidas Alevizos and noone can imagine the great quality of life he gave me. His history with me was always his absolute concern for my digestive problems and there was not a single consultation in which I did not feel understood or supported. His psychology with me was excellent, my post-operative period was very monitored by him and I could not have felt more cared for at the time when I felt most vulnerable.
MLS
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐Grateful from the first moment for the humane treatment that the doctor gave me. He was attentive to any problem or doubt
Agustín H
Your Well-being, Our Expertise