Gallbladder Removal: Procedure and Recovery
Do You Have Gallstones? Here’s Everything You Need to Know About Gallbladder Surgery
The gallbladder is a small but essential organ that stores bile, a digestive fluid necessary for fat digestion. However, certain conditions can affect its function and require its removal through a procedure called cholecystectomy.
When Is Gallbladder Surgery Necessary?
The main reasons for recommending gallbladder surgery are:
🔹Symptomatic Gallstones (Cholelithiasis):
Gallstones form when substances in the bile harden inside the gallbladder. They can cause episodes of abdominal pain, often after eating fatty or heavy meals. If left untreated, gallstones may lead to inflammation, infection, or other serious complications.
🔹Gallbladder Polyps:
These are small growths that develop on the inner wall of the gallbladder. Most are harmless, but removal of the gallbladder is recommended if they grow larger than 10 mm, have irregular features, or cause symptoms — since in rare cases they may become malignant or lead to other complications.
What Happens If It Is Not Treated in Time?
If surgery is not performed when necessary, complications may arise, such as:
🔹Cholecystitis: Acute inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by bile duct obstruction due to gallstones. It can cause severe pain in the right side of the abdomen, fever, nausea, and vomiting. If untreated, it may lead to serious infection or gallbladder perforation.
🔹Biliary Colic: Episodes of intense pain in the upper right or middle abdomen, which may radiate to the back or right shoulder. This occurs when a gallstone temporarily blocks the cystic duct or the common bile duct. It often happens after eating fatty foods and can last from 30 minutes to several hours.
🔹Bile Duct Obstruction: A blockage that prevents the normal flow of bile from the liver to the small intestine. This can cause jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, pale stools, itching, and abdominal pain. If untreated, it can lead to serious infections such as cholangitis.
🔹Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas due to gallstones blocking the pancreatic duct. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain radiating to the back, nausea, vomiting, and fever. This condition can range from mild to severe, with potential life-threatening complications.
These conditions can cause severe pain, infections, and even irreversible damage to organs such as the liver and pancreas. To prevent these risks, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is recommended for patients with recurrent symptoms.
What Is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
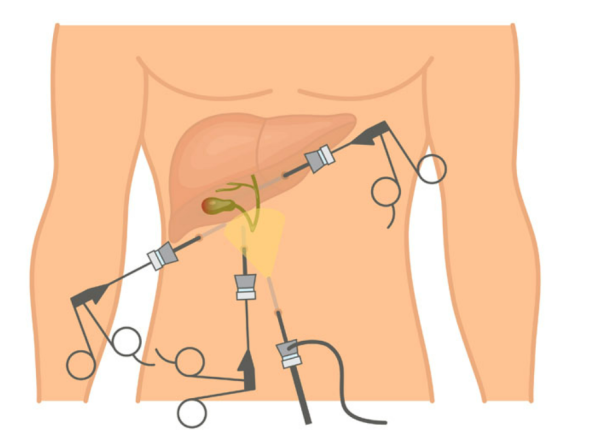
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive procedure in which the gallbladder is removed through small incisions in the abdomen. A small camera and specialized surgical instruments are used to perform the surgery with precision and safety. 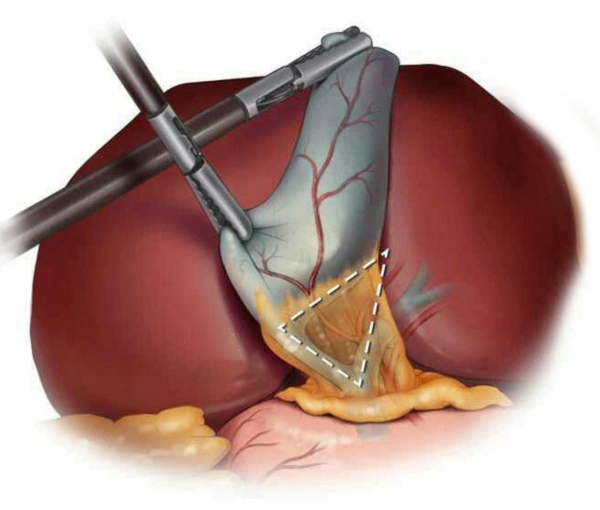
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
🔹Less postoperative pain.
🔹Faster recovery (usually within a few days).
🔹Lower risk of infections and minimal scarring.
🔹Short hospital stay (most cases require only 24 hours).
When Should You See a Specialist?
If you experience recurrent abdominal pain, discomfort after eating, or have been diagnosed with gallstones or gallbladder polyps, it is essential to consult a specialist in general and digestive surgery.
Early diagnosis and timely intervention can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
Book a personalized consultation and get clear answers about your treatment options
Patients Reviews
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Dr. Alevizos is incredible. He explains everything patiently and always with a great attitude. From the very first minute, he made me feel calm and in good hands. You can tell he genuinely cares about how you’re doing and not just about solving the problem quickly. If you’re looking for a surgeon who truly cares about you and is amazing at what he does, he’s the one.
Carlos B
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ A great professional from the very beginning. During the consultations, he thoroughly understood my case, always approachable and reassuring. The procedure went as well as expected, and with the treatment I’m following, I’ve improved significantly.
I’m truly grateful to have been in good hands.
Manu P
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ For me, it has been an enormous stroke of luck to put myself in his hands for a pathology that is so difficult to treat and complicated to resolve. My most sincere thanks and all my love to Dr. Alevizos
NGQ
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ I have been operated on twice by Dr. Alevizos, and without a doubt, he is a great professional who is caring and deeply involved with his patients. I felt absolute peace of mind in his hands. Thank you for everything, Dr. Leonidas!
Francisco J
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Without a doubt, Dr. Leonidas is a spectacular surgeon, in addition to providing gentle, kind and reliable treatment. I was lucky enough to be operated on by him for a pilionidal cyst after having previously been operated on twice without obtaining good results... until I put myself in the hands of Dr. Leonidas, who thanks to his intervention after almost two years, I am in perfect condition. been and I haven't had any problems again!
Alejandro R
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ His patience, kindness, and professionalism throughout the whole process—from diagnosis to surgery and discharge—gave me peace of mind and helped me cope in the best possible way.
Truly grateful
MTT
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐I had stomach surgery by surgeon Leonidas Alevizos and noone can imagine the great quality of life he gave me. His history with me was always his absolute concern for my digestive problems and there was not a single consultation in which I did not feel understood or supported. His psychology with me was excellent, my post-operative period was very monitored by him and I could not have felt more cared for at the time when I felt most vulnerable.
MLS
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐Grateful from the first moment for the humane treatment that the doctor gave me. He was attentive to any problem or doubt
Agustín H
Your Well-being, Our Expertise